Step 12: While¶
CS20-CP1 Apply various problem-solving strategies to solve programming problems throughout Computer Science 20.
CS20-CP2 Use common coding techniques to enhance code elegance and troubleshoot errors throughout Computer Science 20.
CS20-FP2 Investigate how control structures affect program flow.
Tutorial¶
When we want to repeat some instructions until a certain condition is satisfied, Python gives us a simpler way to write this using a new keyword: while. For example, suppose we want to have Reeborg keep moving until it reaches a wall. Previously, we might have done something like the following:
def move_until_wall():
if front_is_clear():
move()
repeat 42:
move_until_wall()
and hoped that 42 would have been a number of repetitions sufficient to reach a wall. Using while, we can write the following:
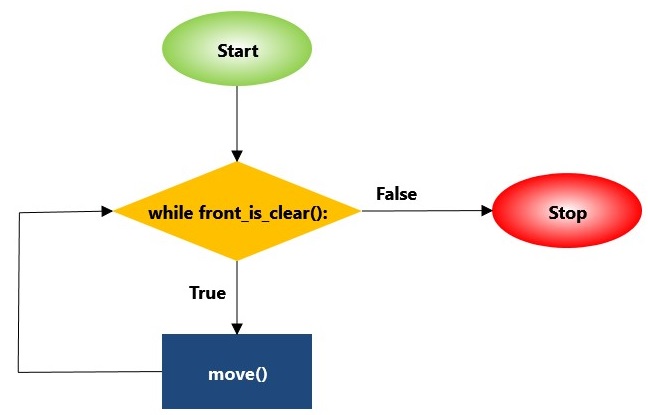
while front_is_clear():
move()
That’s it! No more guessing and asking something to be performed a large number of time just to ensure that it will be enough.
Here’s a flowchart for this simple program:
Your Turn¶
Open Step 12 on the Reeborg environment.
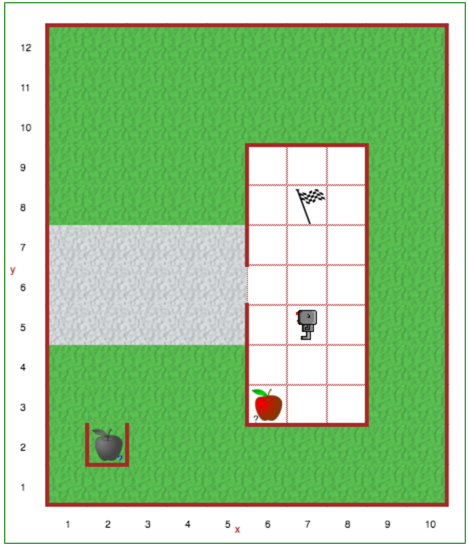
One of Reeborg’s household jobs is to take out the compost. There is, however, a different amount of compost in the container in the house every time Reeborg needs to bring it outside.
Create a program to have Reeborg take out the compost, then return to the house. Reeborg needs to pick up as many rotten apples as are in the compost pail, bring them to the compost container outside, then return to the goal (7, 8). You will need to use while loops in your solution (for the parts that you don’t know until the world loads).