EasyGUI_Qt Reference¶
Caution
EasyGUI_Qt has not been updated in quite some time, and has been causing some teachers issues with installation/use. I am shifting the textbook examples to use FreeSimpleGUI instead, which is an active project (as of now, May 2024). I’ve left this EasyGUI_Qt reference here for now, in case any teachers want to continue to use EasyGUI_Qt. I will eventually remove this page, once I’ve tested/used FreeSimpleGUI for a few semesters of CS20.
EasyGUI_Qt is inspired by EasyGUI and contains a number of different basic graphical user interface components. The version you are using is forked from https://github.com/aroberge/easygui_qt, and adds just a few changes to make things easier for students to use (improved install process by adding PyQt5 as a dependency, added get_file_name function). The following reference covers a subset of the functions that are most accessible to a student at the CS20 level, so you may want to read the official docs of the original project if you would like to explore more usage options. If you explore the official docs, you may find it useful to know that you can call functions with only some of the arguments (this is called optional arguments). If you do this, however, you need to specify which argument you are passing, like easy.get_string(message="Some prompt/question:", default_response="Some string").
Installation¶
In Thonny, open Tools → Manage Packages and type in cs20-easygui into the search bar, then click Install. This installation will take some time, as part of the installation is the backend graphical rendering engine (PyQt5).
Showing Messages¶
If you call show_message with a single argument, that argument should be a string containing the message you would like to show.
import easygui_qt as easy
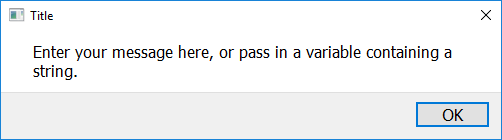
easy.show_message("Enter your message here, or pass in a variable containing a string.")
Additional Options
If you call show_message with a second argument (separated by a comma), that second argument should also be a string, and will be interpreted as the title the pop up window should have.
import easygui_qt as easy
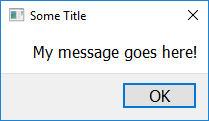
easy.show_message("My message goes here!", "Some Title")
Getting Strings¶
To create a pop up window that prompts the user to enter a string, use the get_string function. This function will return whatever the user types in (as a string). If the user presses Cancel, or closes the window, this function will return None.
import easygui_qt as easy
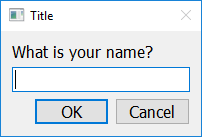
answer = easy.get_string("What is your name?")
Additional Options
If you call get_string with a second argument (separated by a comma), that second argument should also be a string, and will be interpreted as the title the pop up window should have.
import easygui_qt as easy
answer = easy.get_string("What is your name?", "Name")
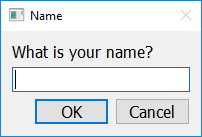
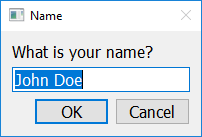
If you call get_string with a third argument (separated by a comma), that third argument should also be a string, and will be interpreted as the default value inside the input box.
import easygui_qt as easy
answer = easy.get_string("What is your name?", "Name", "John Doe")
Getting Integers¶
To create a pop up window that prompts the user to enter an integer, use the get_integer function. This function will return an integer, and forces the user to only enter numbers. If the user presses Cancel, or closes the window, this function will return None.
import easygui_qt as easy
answer = easy.get_integer("How old are you?")
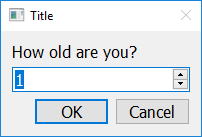
Additional Options
If you call get_integer with a second argument (separated by a comma), that second argument should be a string, and will be interpreted as the title the pop up window should have.
import easygui_qt as easy
answer = easy.get_integer("How old are you?", "Age")
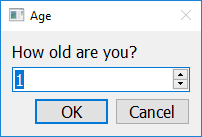
If you call get_integer with a third argument (separated by a comma), that third argument should be an integer, and will be interpreted as the default value inside the input box.
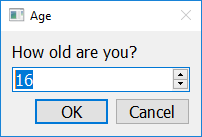
import easygui_qt as easy
answer = easy.get_integer("How old are you?", "Age", 16)
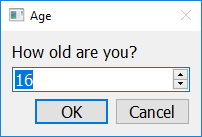
If you call get_integer with five arguments (separated by commas), the fourth argument should be an integer representing the minimum value allowed, and the fifth argument should be an integer representing the maximum value allowed.
import easygui_qt as easy
answer = easy.get_integer("How old are you?", "Age", 16, 0, 120)
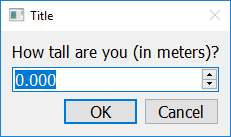
Getting Floats¶
To create a pop up window that prompts the user to enter an float, use the get_float function. This function will return a float, and forces the user to only enter numeric values. If the user presses Cancel, or closes the window, this function will return None.
import easygui_qt as easy
answer = easy.get_float("How tall are you (in meters)?")
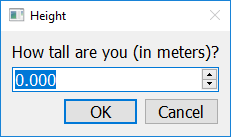
Additional Options
If you call get_float with a second argument (separated by a comma), that second argument should be a string, and will be interpreted as the title the pop up window should have.
import easygui_qt as easy
answer = easy.get_float("How tall are you (in meters)?", "Height")
If you call get_float with a third argument (separated by a comma), that third argument should be a float, and will be interpreted as the default value inside the input box.
import easygui_qt as easy
answer = easy.get_float("How tall are you (in meters)?", "Height", 1.82)
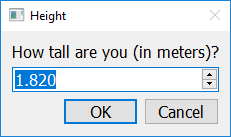
If you call get_float with five arguments (separated by commas), the fourth argument should be a number (int or float) representing the minimum value allowed, and the fifth argument should be a number (int or float) representing the maximum value allowed.
import easygui_qt as easy
answer = easy.get_float("How tall are you (in meters)?", "Height", 1.82, 0.22, 2.72)
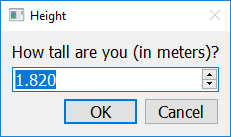
If you call get_float with six arguments (separated by commas), the sixth argument should be an integer representing the number of decimals allowed.
import easygui_qt as easy
answer = easy.get_float("How tall are you (in meters)?", "Height", 1.82, 0.22, 2.72, 2)
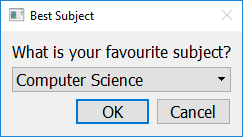
Getting Selection from Drop-Down List¶
To create a pop up window that prompts the user to select an option from a drop-down list, use the get_choice function. This function will return a string containing the user’s choice. If the user presses Cancel, or closes the window, this function will return None.
This function requires three arguments, the prompt message (as a string), the window title (as a string), and the choices the user can choose from (as a list).
import easygui_qt as easy
prompt = "What is your favourite subject?"
title = "Best Subject"
choices = ["Computer Science", "Math", "Phys Ed", "English", "History"]
reply = easy.get_choice(prompt, title, choices)
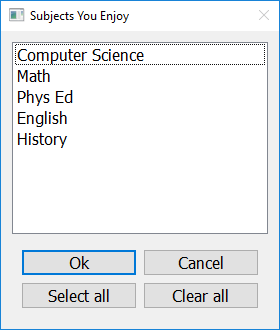
Getting Multiple Selections from List¶
To create a pop up window that prompts the user to select an option (or more than one option) from a list, use the get_list_of_choices function. This function will return a list containing the user’s choices. If the user presses Cancel, closes the window, or does not select any options, this function will return an empty list.
This function requires two arguments, the window title (as a string), and the choices the user can choose from (as a list).
import easygui_qt as easy
prompt = "Subjects You Enjoy"
choices = ["Computer Science", "Math", "Phys Ed", "English", "History"]
reply = easy.get_list_of_choices(prompt, choices)
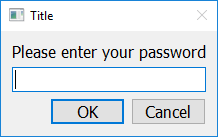
Getting A Password¶
To create a pop up window that prompts the user to enter a password, use the get_password function. This function will return a string containing the user’s input. If the user presses Cancel, or closes the window, this function will return None.
import easygui_qt as easy
reply = easy.get_password("Please enter your password")
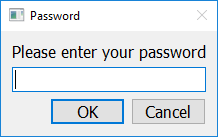
Additional Options
If you call get_password with a second argument (separated by a comma), that second argument should be a string, and will be interpreted as the title the pop up window should have.
import easygui_qt as easy
reply = easy.get_password("Please enter your password", "Password")
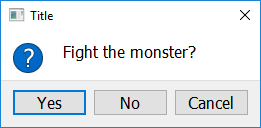
Getting A Yes/No Answer¶
To create a pop up window that prompts the user to answer either Yes or No, use the get_yes_or_no function. This function will return a boolean (True if they clicked Yes, False if they clicked No). If the user presses Cancel, or closes the window, this function will return None.
import easygui_qt as easy
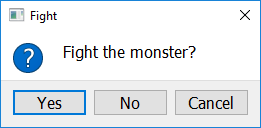
reply = easy.get_yes_or_no("Fight the monster?")
Additional Options
If you call get_yes_or_no with a second argument (separated by a comma), that second argument should be a string, and will be interpreted as the title the pop up window should have.
import easygui_qt as easy
reply = easy.get_yes_or_no("Fight the monster?", "Fight")
Getting An RGB Color Value¶
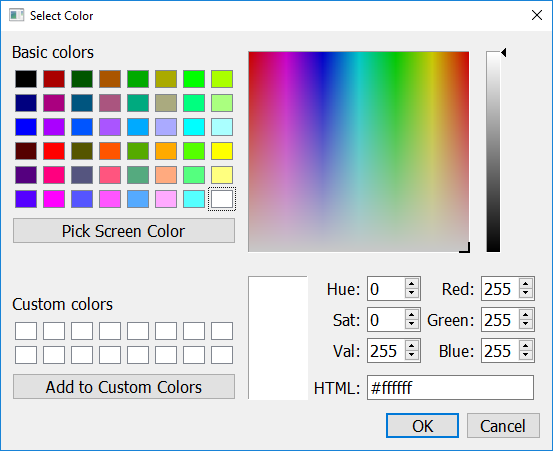
To create a pop up window that prompts the user to select a color, use the get_color_rgb function. This function will return a list with the RGB values of the selected color. If the user presses Cancel, or closes the window, this function will return None.
import easygui_qt as easy
color = easy.get_color_rgb()
r = color[0] # access the amount in the red channel
g = color[1] # access the amount in the green channel
b = color[2] # access the amount in the blue channel
Get File Name Path¶
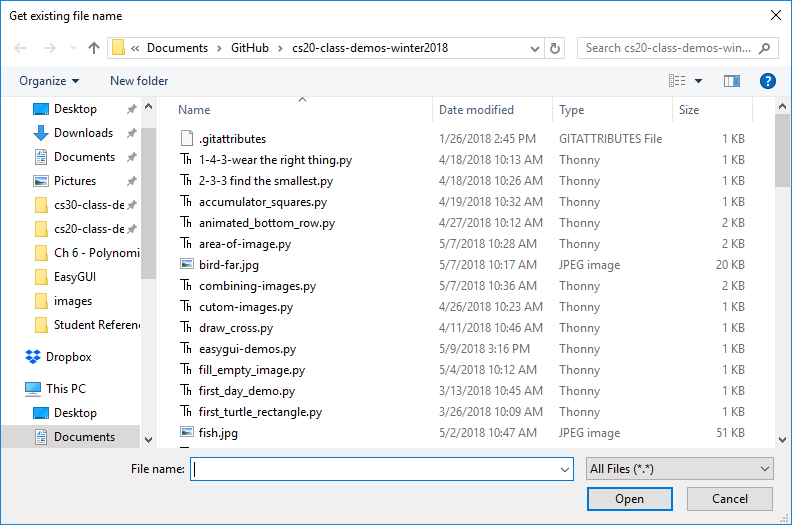
To create a pop up window that prompts the user to select a file from their computer, use the get_file_name function. This function will return a string containing the full path to the file they selected. If the user presses Cancel, or closes the window, this function will return an empty string ''.
import easygui_qt as easy
selected_image = easy.get_file_name()
Additional Options
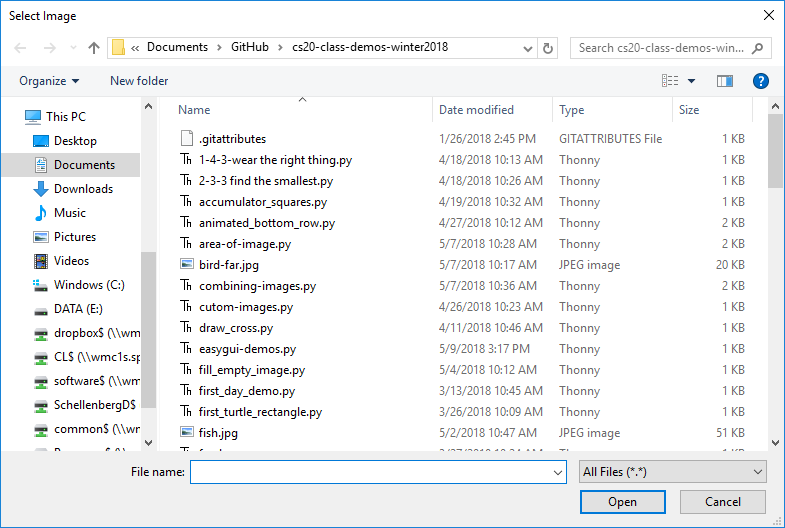
If you call get_file_name with a second argument (separated by a comma), that second argument should be a string, and will be interpreted as the title the pop up window should have.
import easygui_qt as easy
selected_image = easy.get_file_name("Select Image")
Display HTML Formatted Text¶
To create a pop up window that shows rendered HTML, use the show_html function.
This function requires two arguments, the window title (as a string), and the HTML to render (also a string).
import easygui_qt as easy
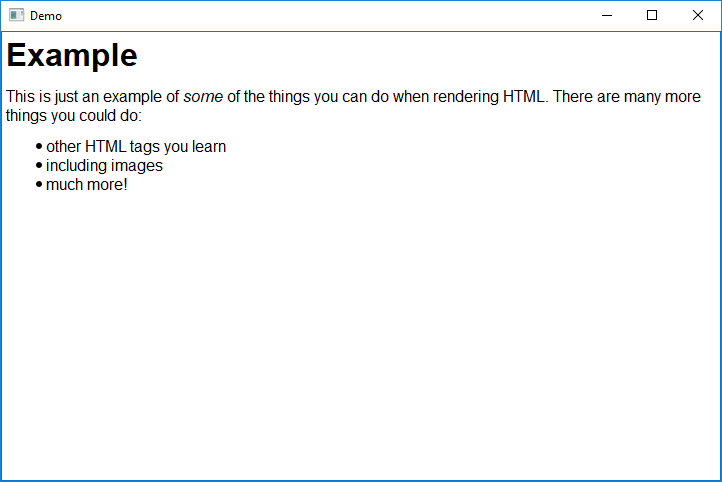
some_html = """
<h1>Example</h1>
<p>This is just an example of <em>some</em> of the things you can
do when rendering HTML. There are many more things you could do:</p>
<ul>
<li>other HTML tags you learn</li>
<li>including images</li>
<li>much more!</li>
</ul>"""
easy.show_html("Demo", some_html)
Display HTML Formatted Text¶
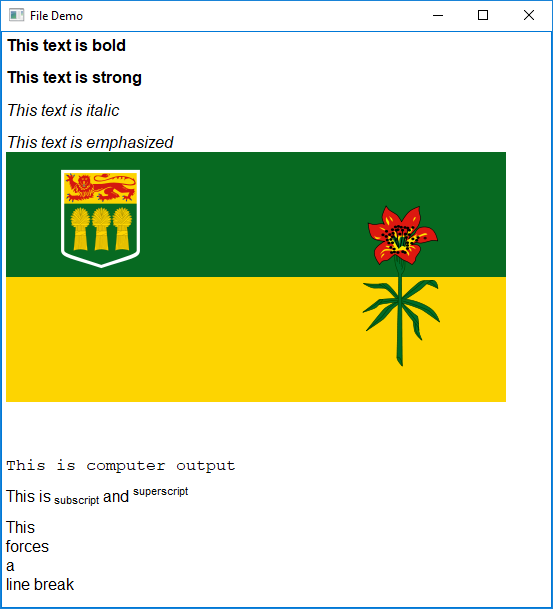
To create a pop up window that shows the contents of a file as rendered HTML, use the show_file function.
This function requires three arguments, the path of the file (as a string), the window title (as a string), rendering engine to use (also a string).
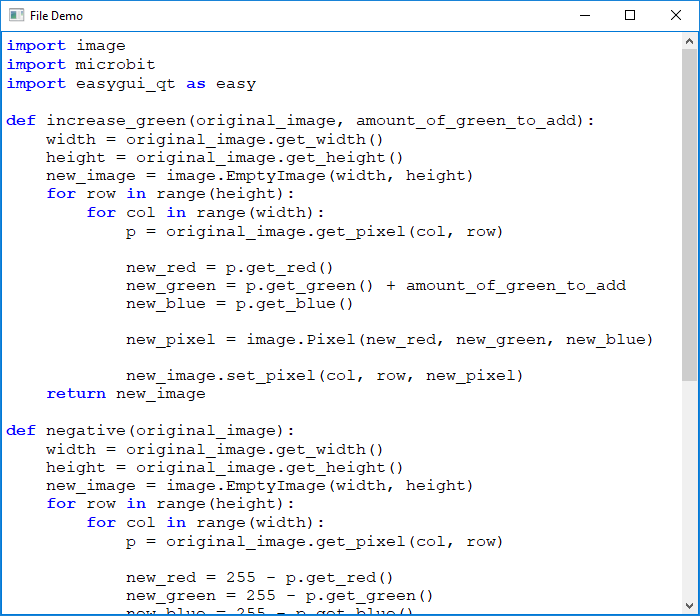
import easygui_qt as easy
file = "path/to/index.html"
easy.show_file(file, "File Demo", "html")
Additional Options
When calling the show_file function, you can choose between the following rendering engines:
textcodehtmlpython
import easygui_qt as easy
file = "path/to/some_script.py"
easy.show_file(file, "File Demo", "python")